Lung Biopsy
A lung biopsy is a medical procedure in which a small sample of lung tissue is removed and examined under a microscope. It is an essential diagnostic tool used to evaluate abnormal lung findings on imaging tests and confirm conditions like lung cancer, infections, interstitial lung disease, or other chronic lung disorders.
Types of Lung Biopsy:
Transbronchial Biopsy:
Performed during bronchoscopy using a flexible tube to take samples from the lungs without surgery.
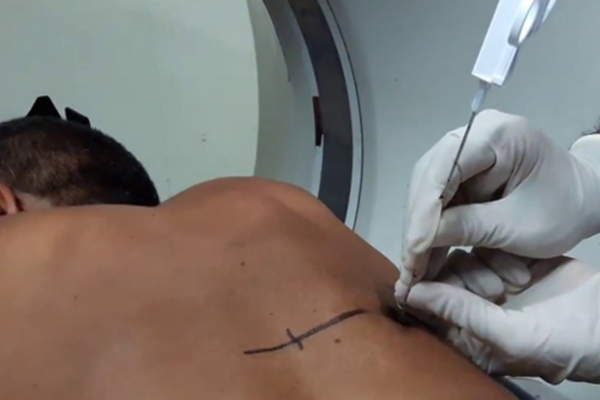
CT-Guided Needle Biopsy:
A minimally invasive procedure where a needle is inserted through the chest wall under CT scan guidance to obtain tissue from a suspicious lung nodule or mass.
Thoracoscopic (VATS) Biopsy:
Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery used for deeper or complex lung lesions, performed through small chest incisions.
Open Surgical Biopsy:
In rare cases, an open chest surgery may be required for a large or difficult-to-access lesion.
Why a Lung Biopsy May Be Recommended:
Evaluate abnormal shadows or masses on chest X-rays or CT scans
Diagnose infections, inflammatory conditions, or interstitial lung disease
Confirm or rule out lung cancer
Guide appropriate treatment based on specific findings